I ran an eval. Now what?
So you built an AI application, curated an initial set of test examples, picked a scoring function, and ran an eval. You got a score—great!
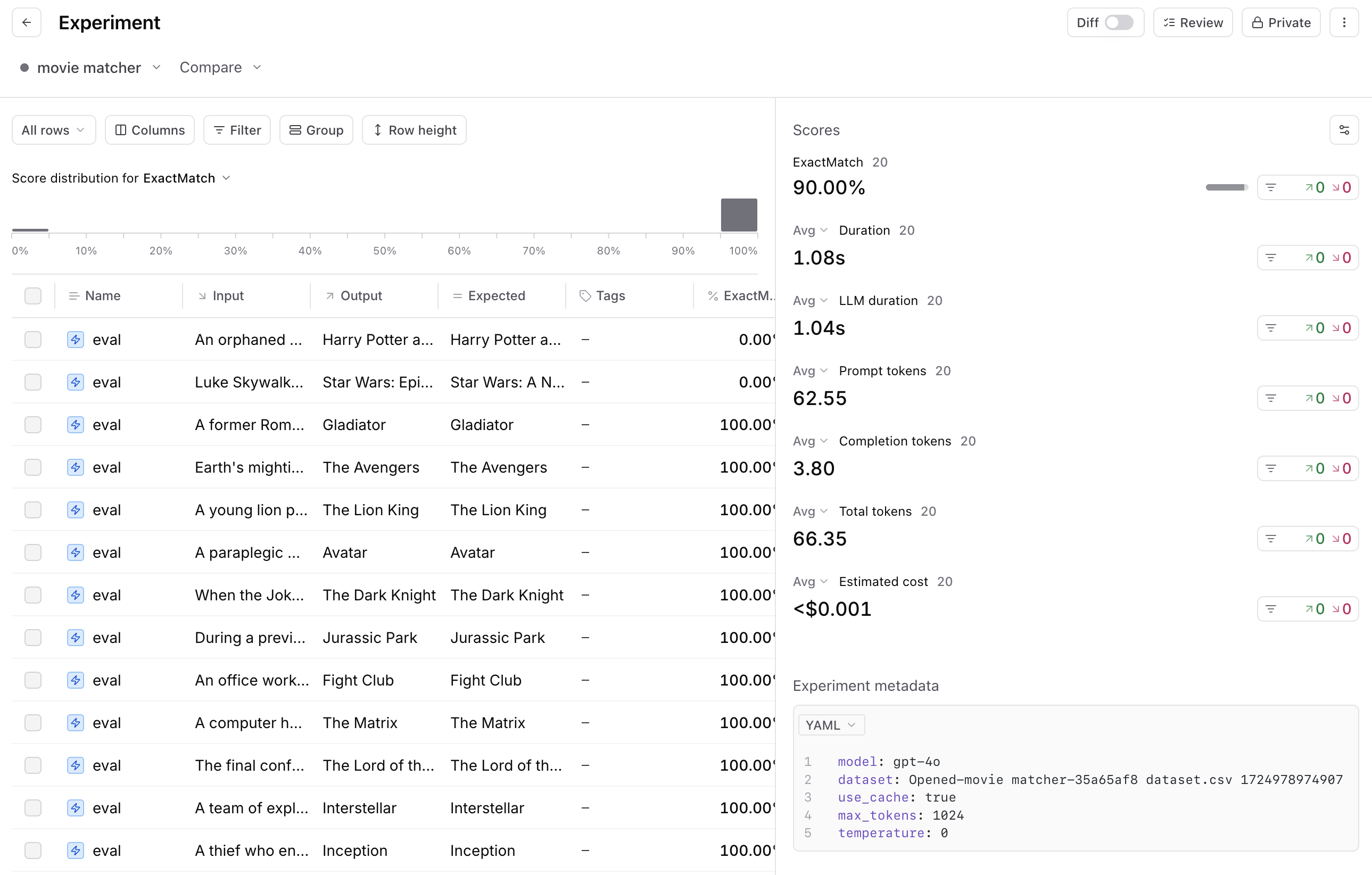
Now what?
We'll walk you through how to think about that score, and more importantly, what steps you should take next to continuously improve both your AI application and your evaluation process, including:
- How to determine what to focus on next
- How to iteratively improve your evals and AI application
- Best practices for creating a rapid development loop
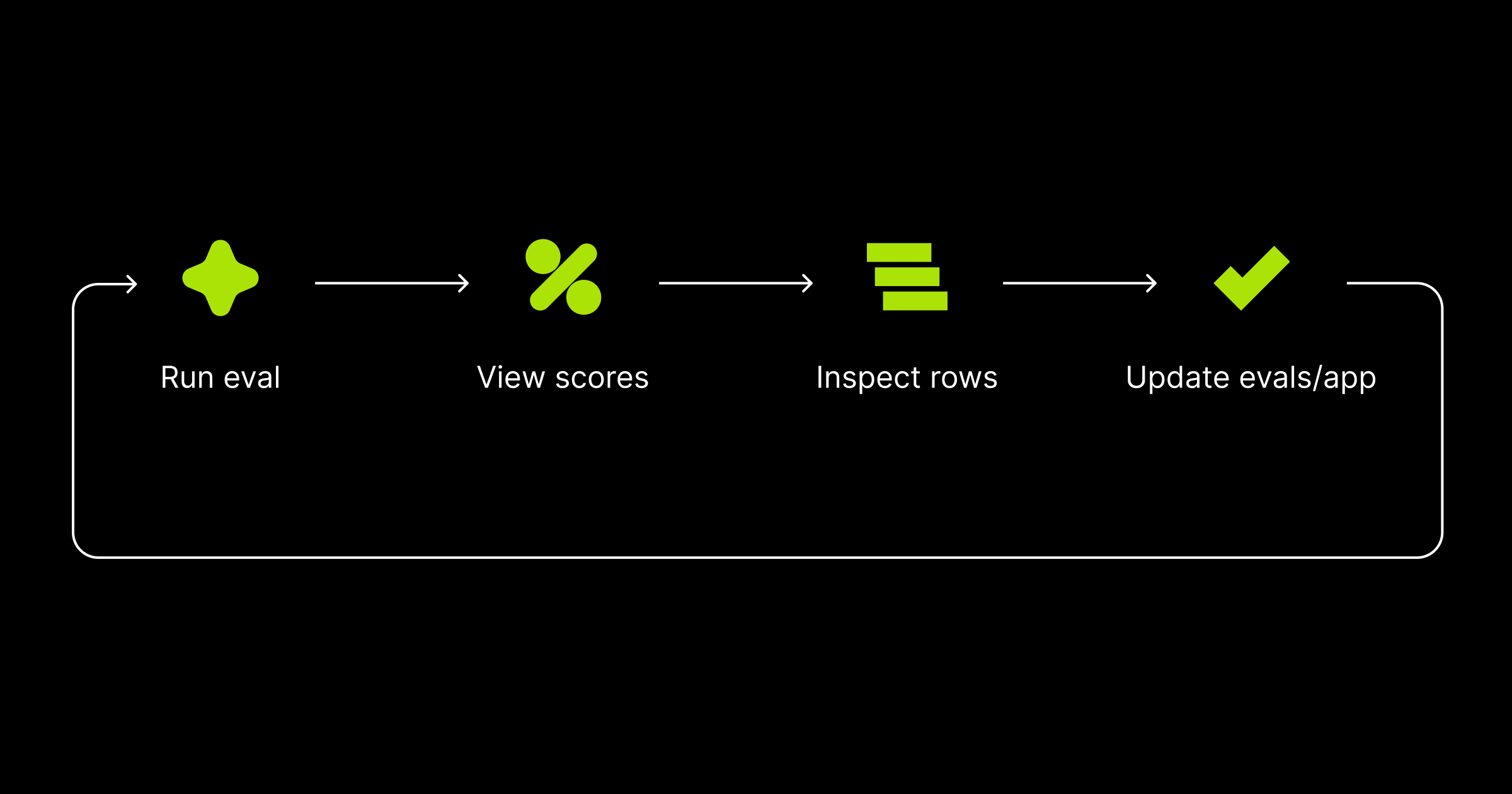
Note: this guide assumes you already have a basic evaluation infrastructure in place. If not, we recommend starting with these two guides first: Structuring evals and Getting started with automated evals.
How to choose your focus
After running an eval, your two goals should be to:
- Improve the fidelity and coverage of your evaluations
- Improve your AI application directly
To figure out where to focus first, start by reviewing 5-10 actual examples from your evals. For each row, inspect the trace–the input, output, and how your evaluation function scored the output.
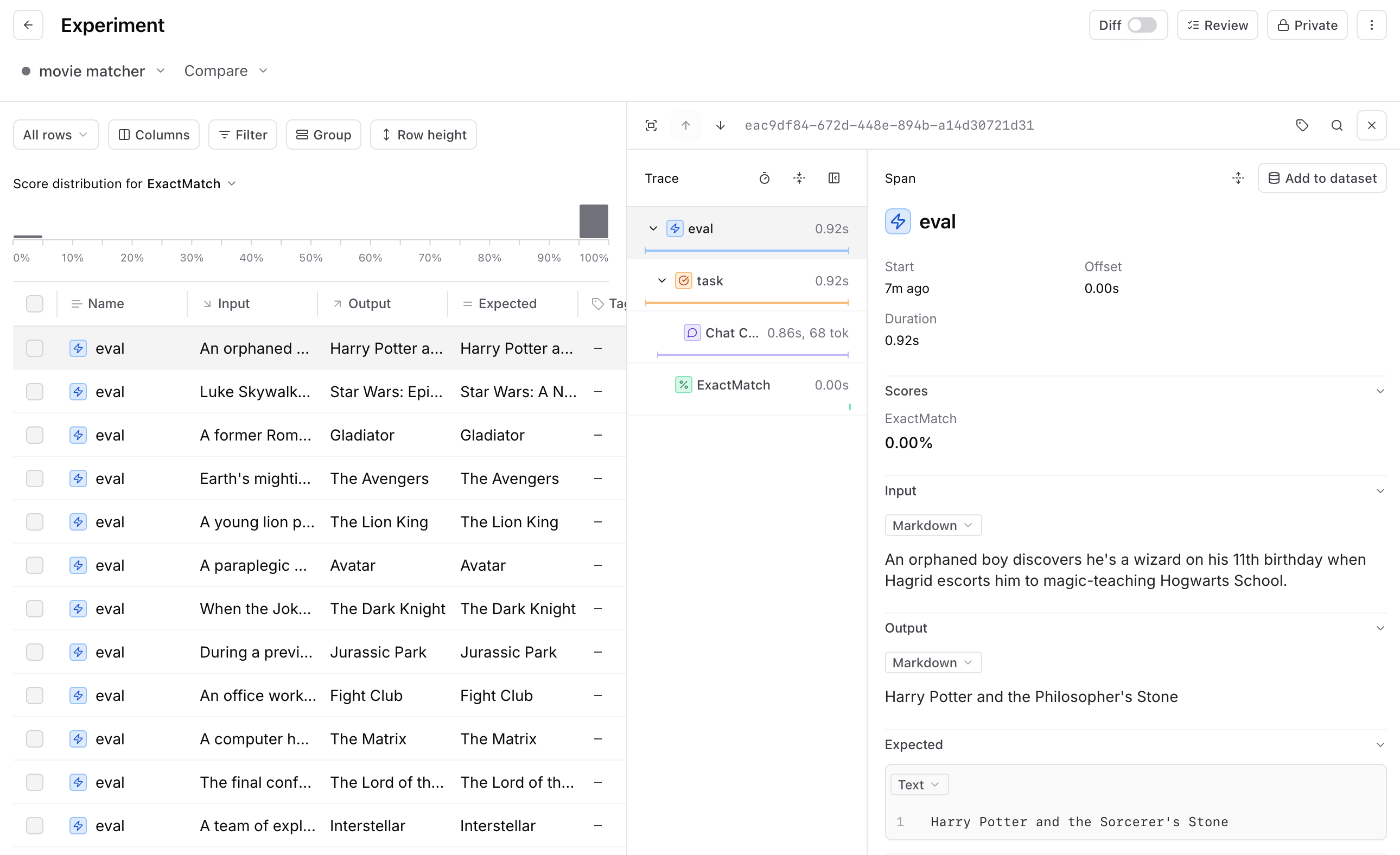
As you review these examples, ask yourself:
- Is the output good or bad?
- Did the scoring function correctly identify it as good or bad?
Every example will fall into one of these four categories:
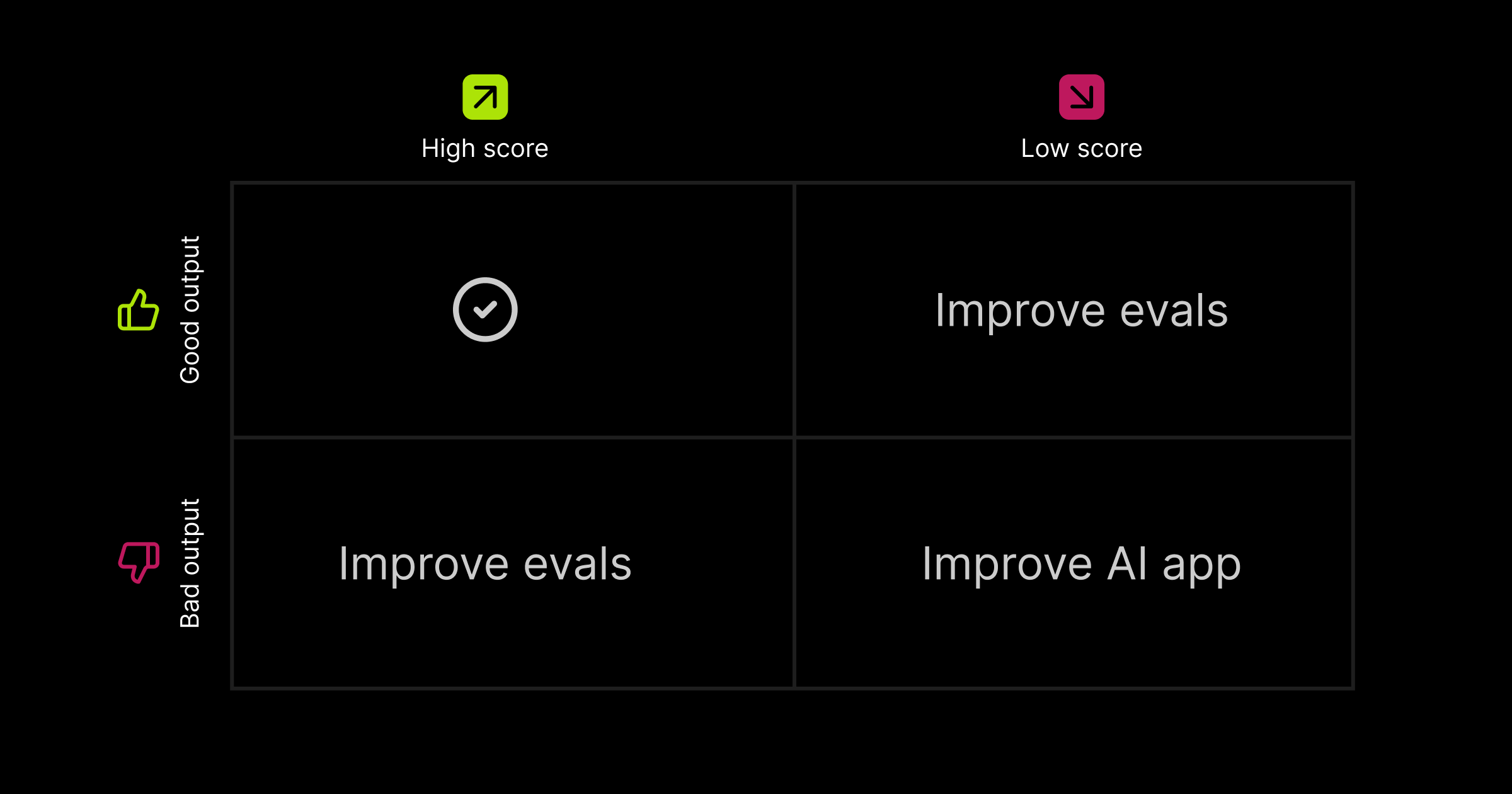
Once you've analyzed these examples, you'll start to notice patterns around how your application is performing and whether your scoring is accurate. From there, you can decide whether to refine your evals or make changes to your application.
The key here is iteration. Don’t overthink it! In almost all cases, it’s worth spending time improving both your evals and your AI application. Move fast, try things out, inspect the results, and roll back updates if necessary.
How to improve your evals
There are three main ways to improve your evals:
- Refine the scoring function to ensure it accurately reflects the success criteria.
- Add new scoring functions to capture different performance aspects (for example, correctness or efficiency).
- Expand your dataset with more diverse or challenging test cases.
For an in-depth guide, check out the full blog post.
How to improve your AI application
If your evaluations are robust, you can confidently iterate on your AI application, since any changes are tested for performance impact and potential regressions each time you re-run your evals.
Here's the general workflow for making improvements:
- Decide on an improvement
- Think through how to make that improvement
- Make the update and re-run your evals to verify results
Decide on an improvement
Before you make an update, it's important to define what you're improving and why. This clarity is important because it makes your iteration targeted and measurable. Start by examining your eval results: overall scores, individual examples, and feedback.
- Low scores: these often highlight underperforming areas or bugs, making them prime targets for improvement
- Random and high scores: potential edge cases or unexpected issues
- Patterns: indications of where systemic improvements can be made
Once you've identified a potential improvement, frame it in one of two ways:
Increase a score
Well-defined scores are tied to specific attributes (e.g. factuality, length of output) or capabilities (e.g. selecting the right tool, writing executable code). By increasing a score, you're clearly indicating that you are improving your application along a particular axis. Start with end-to-end scores—these give you a broad view of how well your system is performing. Then, as needed, zoom in on specific sections where smaller, more focused changes can make a significant impact.
Fix a specific set of bad outputs
Fixing examples of bad outputs is essential when dealing with customer complaints or catching critical failures while inspecting examples. These fixes typically address very visible or user-facing problems, so they're usually high leverage.
Think through how to make that improvement
Once you've decided what to improve, the next step is to think through what update would result in the improvement you decided on. This part of the process is critical because the range of potential tweaks is broad, but choosing the right one can be both fun and challenging.
Here are some common areas we see AI teams change:
- Prompts (e.g. wording, in-context examples, OpenAI guide)
- Model weights (fine-tuning)
- Retrieval pipeline (embedding model, chunking, re-ranking, # of documents retrieved)
- Non-LLM code (e.g. pre/post processing, routing)
- API call parameters (e.g. function-calling, temperature, max tokens)
- Tool usage
- Base model
Make the update and re-run your evals to verify results
Now, it's time to make the update to your AI application. Whether you’re tweaking a prompt, adjusting model weights, or modifying pipeline logic, the goal is to introduce changes that directly target the performance or behavior you’re trying to improve.
After implementing the change, re-run your evals to see if your change to verify the impact.
- If your goal was to improve a specific score/attribute, you should check that score
- If your goal was to fix a specific customer problem, you should inspect examples relevant to that problem
Importantly, you should also closely monitor your overall scores to ensure you are not regressing in other areas. Avoiding unintended regressions is critical to continuous forward progress.
Repeat!
Did the change move the needle? Great—build on that momentum. If not, you now have more data to make better decisions and try again. The key is in the iteration—every cycle moves your application and evals closer to optimal performance.
Ideal workflow
We've shared how critical a rapid development loop is to delivering high-quality AI features. After each improvement, re-run your evaluations and go through the workflow again.
Many of our customers cycle through this loop 50+ times a day. This fast-paced iteration is what enables AI teams to stay ahead, ship robust AI features, and quickly react to feedback and issues. To see an example of the workflow in action, check out how Notion develops world-class AI features.
At Braintrust, our goal is to make AI development as iterative and robust as possible. If you're looking to optimize your workflow or scale your AI product development efforts, get in touch!